Standing on the shoulders of giants |April 3, 2023|
tags: math.OC
One of the most illuminating activities one can undertake is to go back in time and see how the giants in (y)our field shaped the present. Sadly, several of our giants passed away recently and I want to highlight one of them in particular: Roger W. Brockett.
It is very rare to find elegant and powerful theories in sytems and control that are not related to Brockett somehow, better yet, many powerful theories emerged directly from his work. Let me highlight five topics/directions I find remarkably beautiful:
(Lie algebras): As put by Brockett himself, it is only natural to study the link between Lie theory and control theory since the two are intimately connected through differential equations |1.2|. ‘‘Completing this triangle’’ turned out to be rather fruitful, in particular via Frobenius’ theorem. Brockett played a key role in bringing Lie theoretic methods to control theory, a nice example is his 1973 paper on control systems on spheres (in general, his work on bilinear systems was of great interest) |5|.
(Differential geometric methods): Together with several others, Brockett was one of the first to see how differential geometric methods allowed for elegantly extending ideas from linear control (linear algebra) to the realm of nonlinear control. A key event is the 1972 conference co-organized with David Mayne |1|. See also |2| for a short note on the history of geometric nonlinear control written by Brockett himself.
(Brockett's condition): After pioneering work on (local) nonlinear controllability in the 70s it was observed (by means of low-dimensional counterexamples) that controllability is not sufficient for the existence of a stabilizing continuous feedback. This observation was firmly established in the (1982) 1983 paper by Brockett |3| where he provides his topological necessary condition (Theorem 1 (iii)) for the existence of a stabilizing differentiable feedback, i.e.
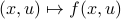 must be locally onto (the same is true for continuous feedback). Formally speaking, this paper is not the first (see Geometrical Methods of Nonlinear Analysis and this paper by Zabczyk), yet, this paper revolutionized how to study necessary conditions for nonlinear stabilization and inspired an incredible amount of work.
must be locally onto (the same is true for continuous feedback). Formally speaking, this paper is not the first (see Geometrical Methods of Nonlinear Analysis and this paper by Zabczyk), yet, this paper revolutionized how to study necessary conditions for nonlinear stabilization and inspired an incredible amount of work.
(Nonlinear control systems): Although we are still far from the definitive control system (modelling) framework, Brockett largely contributed to a better understanding of structure. Evidently, this neatly intertwines with the previous points on bilinear systems (Lie algebras) and differential geometry, however, let me also mention that the fiber bundle perspective (going beyond Cartesian products) is often attributed to Brockett |4|.
(Dynamical systems perspective on optimization): We see nowadays still more and more work on the continuous-time (and system theoretic) viewpoint with respect to optimization algorithms. One can argue that Brockett was also of great importance here. It is not particularly surprising that one can study gradient flows to better understand gradient descent algorithms, however, it turned out that one can understand a fair amount of routines from (numerical) linear algebra through the lens of (continuous-time) dynamical systems. Brockett initiated a significant part of this work with his 1988 paper on the applications of the double bracket equation
![dot{H}=[H,[H,N]]](eqs/229228239358215717-130.png) |6|. For a more complete overview, including a foreword by Brockett, see Optimization and Dynamical Systems.
|6|. For a more complete overview, including a foreword by Brockett, see Optimization and Dynamical Systems.
References (all by Brockett).
|1|: Geometric Methods in System Theory - Proceedings of the NATO Advanced Study Institute held at London, England, August 27-Septernber 7, 1973, ed. with Mayne, D. Reidel Publishing Company (1973).
|1.2|: Chapter: Lie Algebras and Lie groups in Control Theory in |1|.
|2|: The early days of geometric nonlinear control, Automatica (2014).
|3|: Asymptotic stability and feedback stabilization, Differential Geometric Control Theory, ed. with Millman and Sussmann, Birkhäuser (1983).
|4|: Control theory and analytical mechanics, Geometric Control Theory, Lie Groups: History,
Frontiers and Applications, Vol. VII, ed. Martin and Hermann, Math Sci Press, (1976).
|5|: Lie Theory and Control Systems Defined on Spheres, SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics (1973).
|6|: Dynamical systems that sort lists and solve linear programming problems, IEEE CDC (1988).
See also this 2022 interview (video) with John Baillieul and the foreword to this book for more on the person behind the researcher.